Research and development plays a fundamental role in the advancement of science, technology and innovation. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries recognize the importance of encouraging investment in R&D to boost economic growth and improve competitiveness.
In this sense, many countries have implemented a series of tax incentives to promote investment in R&D. These incentives seek to reduce the costs (and cover the risk) associated with research and development, encourage collaboration between companies and research centers, and stimulate the creation of highly qualified jobs in the private sector.
Tax incentives for R&D
One of the most common incentives is the tax deduction for R&D activities. This scheme allows companies to deduct a percentage of R&D expenses from their tax base, which reduces the tax burden and increases the resources available for investment in research and development. Some countries offer additional deductions for the hiring of qualified personnel or for the acquisition of technological equipment.
Another incentive used in many OECD countries is the R&D tax credit. This mechanism allows companies to obtain a tax credit equivalent to a percentage of R&D expenses. Tax credit is a direct benefit that individuals can use to reduce the tax payable or even obtain a cash refund if the credit exceeds the tax owed, unlike tax deduction.
In addition to direct tax incentives, some OECD countries have implemented special regimes for research and development, which offer additional benefits, such as exemption from taxes on income derived from the exploitation of patents or reduction of taxes on profits from patents. capital obtained from the sale of assets related to R&D.
In many cases, R&D tax incentives are designed to encourage collaboration between companies and research centers. For example, some countries allow the transfer of R&D tax credits between companies, facilitating collaboration on joint research projects. Other incentives include the possibility of deducting R&D expenses carried out by third parties, such as universities or research centers, as long as effective collaboration is established.
R&D Tax Incentives Intensity Map
It is important to highlight that tax incentives for R&D vary significantly between different countries. Each country has its own regulatory framework and establishes its own conditions and requirements to access tax benefits. Some countries offer more generous incentives, while others have stricter requirements. Therefore, it is essential that companies interested in taking advantage of these incentives consult the current legislation in each country and obtain appropriate advice.
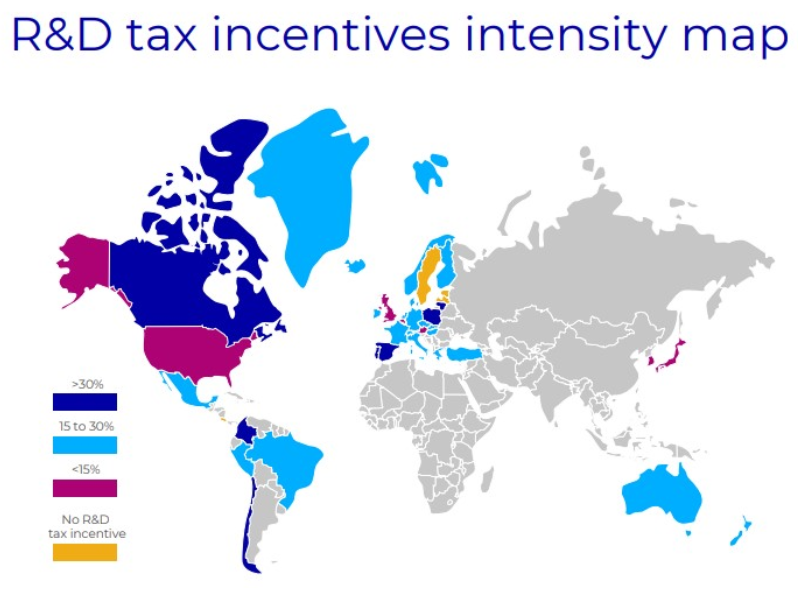
For this map to be representative of the different nature of R&D tax incentives (volume- based and incremental tax credits, super deduction), we took the scenario of a large company with R&D expenses during the last 10 years. Every year the amount of eligible R&D expenses is growing, as such, the claimant can apply for incremental R&D tax credits and deductions. The effective return on the R&D expenses is shown in the legend as a percentage of posttax reduction.
How can FI Group help you?
At FI Group we have extensive knowledge and experience in obtaining these tax incentives on different continents, with a global and coordinated strategy that is also complemented by the management and obtaining of public aid and subsidies for different types of investments. The combination of both incentives, from a strategic point of view and from a financial point of view, can mean for the company an important differentiation and competitive advantage within its scope of action.
FI Group has over 20 years of experience. Our specialized experts are at your disposal to analyze the fit of your project and advise you on obtaining tax incentives. Contact us.
